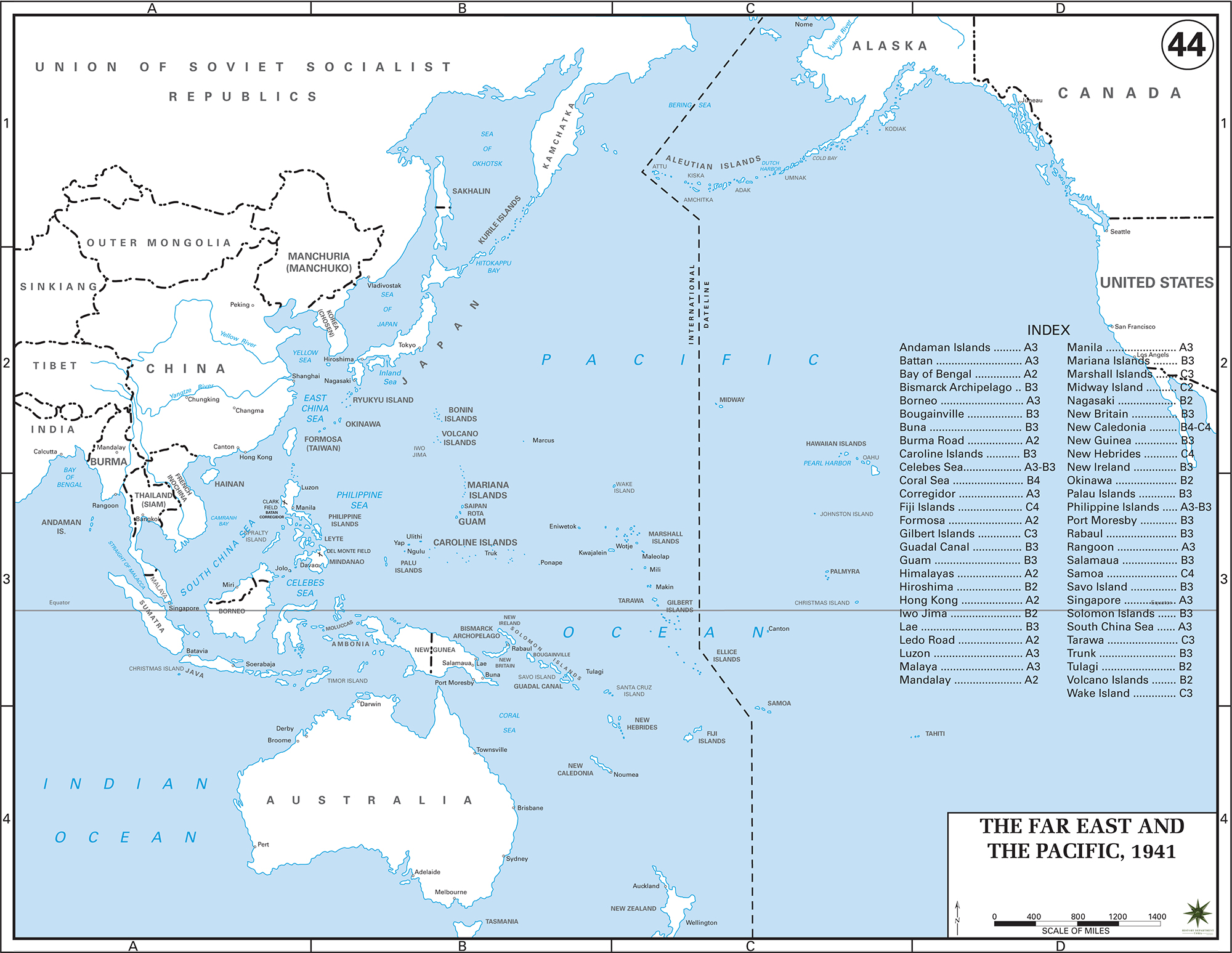
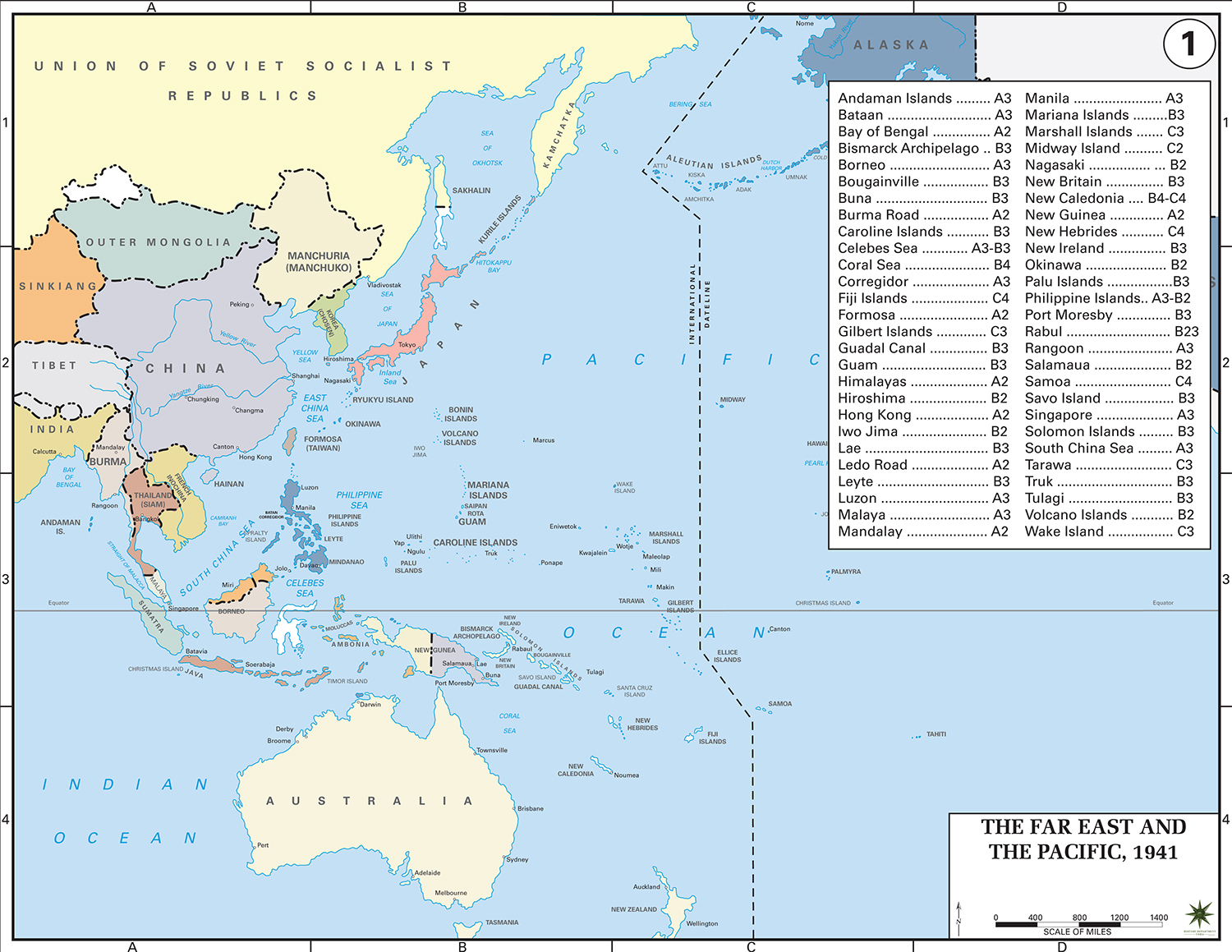
Map Description
Two History Maps of WWII:
The Far East and the Pacific in 1941
Illustrating:
-
Andaman Islands
Occupied by Japan (March 23, 1942) after the fall of Singapore. The islands were occupied without resistance, and the Japanese maintained a heavy garrison, committing severe atrocities against the population.
-
Bataan
Site of the brutal Battle of Bataan (January 7 – April 9, 1942); U.S. and Filipino forces surrendered to Japan; led to the infamous Bataan Death March, a forced march after surrendering to Japanese forces, during which thousands of American and Filipino prisoners.
-
Bay of Bengal
Japanese navy raided the area in the Indian Ocean Raid (March–April 1942), attacking British bases and sinking Allied ships.
-
Bismarck Archipelago
Seized by Japan early in the war (January 1942) and became a major base. Heavy fighting occurred here during the Allied counteroffensives in 1943-44. The Battle of New Britain (December 15, 1943 – August 1945) was part of the Allied campaign to isolate Rabaul.
-
Borneo
Invaded by Japan (December 16, 1941), British and Dutch Borneo was occupied until 1945, its oil fields being a primary strategic objective for the Japanese military. The battles of Borneo involved heavy fighting between Japan and Allied forces. The fighting during the Japanese invasion took place Dec 41 - March 42, and the fighting during the Allied liberation campaign (Operation Oboe) from May 1 - July 21, 1945.
-
Buna
In Papua New Guinea; Battle of Buna-Gona (November 16, 1942 – January 22, 1943); important Allied victory against Japanese forces.
-
Burma Road
Vital supply route from British India to China during the Second Sino-Japanese War and WWII; Japanese aimed to cut it off (closed after May 1942 with fall of Burma).
-
Caroline Islands
Japanese-mandated islands since WWI; fortified bases like Truk Lagoon used heavily; attacked by U.S. (e.g., Operation Hailstone, February 17–18, 1944).
-
Celebes Sea
The Celebes Sea was a strategic waterway important for Japan's resource shipments from conquered territories. Naval operations between U.S./Allies and Japan happened here; near Philippines and Dutch East Indies.
-
Coral Sea
Site of the Battle of the Coral Sea (May 4–8, 1942); first aircraft carrier battle; strategic Allied victory stopping Japan’s advance to Port Moresby (Papua New Guinea), and Australia.
-
Corregidor
Corregidor, an island fortress in Manila Bay, was the last American stronghold to fall in the Philippines in 1942. Following a prolonged siege by Japanese forces, it was captured during the Battle of Corregidor (May 5–6, 1942), a key moment in the fall of the Philippines.
-
Fiji Islands
Allied base during WWII; helped launch operations into Solomon Islands and supported Guadalcanal Campaign.
-
Formosa (modern Taiwan)
Japanese colony since 1895; base for operations against China and later the Philippines; bombed heavily by Allies starting October 1944.
-
Gilbert Islands
U.S. attacked in the Battle of Tarawa (November 20–23, 1943); bloody fight to capture key islands from Japan.
-
Guadalcanal
First major U.S. offensive in Pacific; Battle of Guadalcanal (August 7, 1942 – February 9, 1943); turning point against Japan.
-
Guam
U.S. territory captured by Japan (December 10, 1941); retaken by U.S. in Battle of Guam (July 21 – August 10, 1944).
-
Himalayas
"The Hump" - nickname for dangerous Allied supply flights over Himalayas to bring aid to China after Burma Road closure (starting 1942).
-
Hiroshima
First city targeted by atomic bomb (August 6, 1945).
-
Iwo Jima
Site of bloody Battle of Iwo Jima (February 19 – March 26, 1945); strategic airfield for U.S. bombers.
-
Lae
In New Guinea; captured by Allies during Salamaua–Lae Campaign (September 1943); major Japanese base.
-
Ledo Road
Built by Allies (1942–1945) as an alternative to the Burma Road to supply China.
-
Luzon
Largest island in Philippines; site of major battles; Battle of Luzon (January 9 – August 15, 1945) liberated it from Japan.
-
Malaya
Invaded by Japan (December 8, 1941); fell after Battle of Malaya (ended January 31, 1942); led to fall of Singapore.
-
Mandalay
Key city in Burma; retaken by British during Battle of Mandalay (March 1945).
-
Manila
Capital of Philippines; site of brutal Battle of Manila (February 3 – March 3, 1945); heavy civilian casualties.
-
Mariana Islands
Captured by U.S. in Battle of Saipan (June 15 – July 9, 1944) and other battles; allowed bombing raids on Japan.
-
Marshall Islands
Fortified by Japan; captured by U.S. in Battle of Kwajalein and Battle of Eniwetok (January–February 1944).
-
Midway Islands
Site of the decisive Battle of Midway (June 4–7, 1942); major turning point favoring the Allies.
-
Nagasaki
Second city hit by atomic bomb (August 9, 1945); contributed to Japan’s surrender.
-
New Britain
Part of Bismarck Archipelago; stronghold at Rabaul; subject to Allied isolation strategy starting late 1943.
-
New Caledonia
Important Allied base; protected shipping and supported Guadalcanal operations.
-
New Guinea
Key battleground; major campaigns by Allies (1942–1945) against entrenched Japanese forces.
-
New Hebrides
(Now Vanuatu) used as Allied base during Pacific campaigns.
-
New Ireland
Japanese stronghold near New Britain; isolated rather than directly assaulted by Allies.
-
Okinawa
Site of largest amphibious assault in Pacific: Battle of Okinawa (April 1 – June 22, 1945); bloodiest battle in Pacific War.
-
Palau Islands
U.S. captured Peleliu in bloody Battle of Peleliu (September 15 – November 27, 1944); debated necessity.
-
Philippine Islands
Vital U.S. territory; fell to Japan (1942), then recaptured (1944–1945) in major Allied operations.
-
Port Moresby
Target of Japanese advance; defended successfully in Battle of the Coral Sea and later through ground fighting in New Guinea.
-
Rabaul
Major Japanese base on New Britain; isolated by Allied strategy rather than directly assaulted (1943–1945).
-
Rangoon
Capital of Burma; fell to Japan (March 8, 1942); recaptured by Allies (May 3, 1945).
-
Salamaua
Near Lae; captured by Allies during Salamaua–Lae Campaign (September 1943).
-
Samoa
Used by Allies as a rear base for Pacific operations.
-
Savo Island
Near Guadalcanal; site of disastrous Battle of Savo Island (August 8–9, 1942) - heavy Allied losses.
-
Singapore
Strategic British base; surrendered to Japan (February 15, 1942); major Allied defeat.
-
Solomon Islands
Major campaign area (1942–1945); Guadalcanal and other key battles fought here.
-
South China Sea
Important Japanese shipping route; attacked heavily by U.S. Navy and submarines later in war.
-
Tarawa
Site of bloody Battle of Tarawa (November 20–23, 1943) during Gilbert Islands campaign.
-
Truk
(Also known as Chuuk) - huge Japanese naval base in Caroline Islands; neutralized by Operation Hailstone (February 17–18, 1944).
-
Tulagi
Captured by U.S. Marines early in Guadalcanal Campaign (August 7, 1942).
-
Volcano Islands
Chain including Iwo Jima; fought over during Battle of Iwo Jima.
-
Wake Islands
U.S. territory attacked by Japan (December 8, 1941); fell after Battle of Wake Island (December 23, 1941).
Credits
Courtesy of the United States Military Academy Department of History.
Related Maps
Map of the Pacific 1910Related Links
About the Second Sino-Japanese WarAbout World War II
WWII Timelines
Click map to enlarge.