|

 Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
 Musicians, Painters &
Artists
Musicians, Painters &
Artists
 Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
 Native Americans & The Wild
West
Native Americans & The Wild
West
 First Ladies
First Ladies
 Popes
Popes
 Troublemakers
Troublemakers
 Historians
Historians
 Archaeologists
Archaeologists
 Royal Families
Royal Families
 Tribes & Peoples
Tribes & Peoples

Assassinations in History
Who
got slain, almost slain, when, how,
why, and by whom?
 Go to the
Assassination Archive
Go to the
Assassination Archive




Online History Dictionary A - Z
All-Time Records in
History
What was the
bloodiest battle, the battle with the least
casualties, who was the greatest military leader?
 Go to
Records in History
Go to
Records in History

|
|

Declaration of
Independence: July 4th 1776
American War of Independence 1775 -
1783
The American War of Independence,
also called the American Revolution, or the
American Revolutionary
War, was fought from 1775 until
1783.
|
|
Image Above
Declaration of
Independence: July 4th 1776. Lithograph, hand
colored. N. Currier (Firm),
created between 1835 and 1856. Library of
Congress.
The American Revolution in a Nutshell
Thirteen mainland colonies of British North America declared their
independence on July 4, 1776, to form the United States of America.
The War of Independence started as a civil war but soon became an
international war when France, Spain, and the Netherlands joined the
colonies against Britain.
And here is the map:
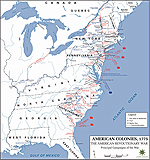
Map of the Principal Campaigns
of the American Revolution
|
Key Issues
of the American Revolution
During the
 French and Indian Wars, Britain had spent quite some money
for the colonies' defense and attempted to get repayment. French and Indian Wars, Britain had spent quite some money
for the colonies' defense and attempted to get repayment.
The colonies argued that Britain would have the right to impose
taxes, so long as the colonies were represented in Parliament;
therefore, taxation without representation was unacceptable. The
tone became sharper on both sides and a boycott of British goods was
discussed in the colonies.
Unrest increased as colonial radicals purposely fueled the dispute
to break with Britain. They argued that the Empire generally handled
political and economical issues detrimental to their interest. The
Boston Massacre in 1770 and the
 Boston Tea Party in 1773 were an
indicator of the growing tension. Boston Tea Party in 1773 were an
indicator of the growing tension.
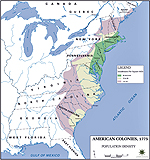
American Colonies: Population Density 1775
What Started the
American Revolution?
The
Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, were the
beginning of the American Revolution.
To avoid armed rebellion, a British force came to seize colonists'
weapons at Concord, a town near Boston. The colonists had been
forewarned and intercepted the British at Lexington Green. Shots
were exchanged, and some Americans were killed.
Arriving at Concord, the British were confronted and outnumbered by
the colonial militia and had to withdraw to Boston while being
attacked on all sides.
Number of casualties in the battles of
Lexington and Concord:
British: 73 killed, 174 wounded, 26 missing
American: 93 dead, wounded, or missing (some say 95)
The Americans were ready to drive the
British out of Boston and started the
 Siege of Boston. Siege of Boston.
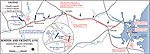
Map of the Battle of Lexington and Concord
April 19, 1775
What Ended the
American Revolution?
The last major battle took place on October 19, 1781. It ended with
the surrender of British General Corwallis at Yorktown, Virginia.
However, for all parties to negotiate acceptable terms required some
time.

Battle of Guilford Court House,
March 15, 1781
The American Revolution officially ended with the
 Peace of Paris 1783. Great Britain acknowledged the
independence of the United States, with the Mississippi River as the
western boundary. Navigation on the river remained open to both
nations.
Peace of Paris 1783. Great Britain acknowledged the
independence of the United States, with the Mississippi River as the
western boundary. Navigation on the river remained open to both
nations.

The Surrender of Lord Cornwallis
at Yorktown, Virginia, October 19, 1781.
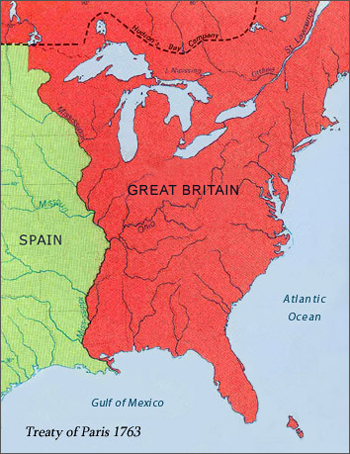
Map of North America After the 1763 Treaty of Paris
 Treaty of Paris 1763
Treaty of Paris 1763
Library of Congress
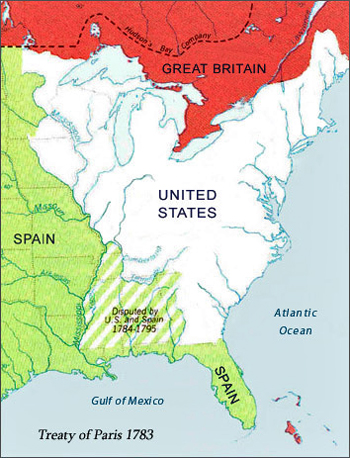
Map of North America
After the 1783 Treaty of Paris
 Treaty of Paris 1783
Treaty of Paris 1783
Library of Congress
Casualties of the
American Revolution
Estimates differ. Some historians say that the Revolution claimed a
total of 25,000 lives. Others estimate American losses at 4,400,
British losses 6,800, and German losses at 1,200.
 Check the American war casualties report
Check the American war casualties report
What Impact Did the
American Revolution Have?
The American Revolution caused many Europeans to reassess their own
government. The idea that a country actually could decide upon its
government was exciting and appealed especially to those in lower
social classes.
American Revolution
Trivia
To remedy a lack of troops, the British hired the services of
approximately 30,000 German mercenary soldiers. The majority of the
Germans came from the German state Hesse-Cassel; thus they became
known as the Hessians.
How much did this war cost?
 Check the
costs of major US wars in comparison. Check the
costs of major US wars in comparison.
And here is a map of the campaigns of
the American Revolution:
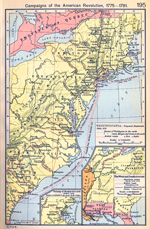
AMERICAN REVOLUTION
Click on map to enlarge
The Battles of
the American Revolution
|
1775,
April 19 |
Battles of Lexington and
Concord, American victory

Map of the Battle of
Lexington and Concord
|
|
1775,
April 20 - 1776, March 17 |
Siege of Boston, American victory
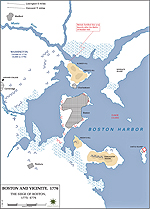
Map of the Siege of Boston
|
|
1775,
June 17 |
Battle of Bunker Hill, Massachusetts, British victory
(also called Battle of Breed's Hill)
Trivia: Wee
 John Quincy Adams
watched the Battle of Bunker Hill from the top of Penn's
Hill above the family farm.
John Quincy Adams
watched the Battle of Bunker Hill from the top of Penn's
Hill above the family farm.
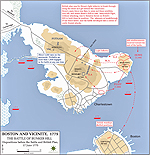
Map of the Battle of Bunker Hill
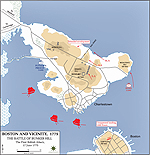
Battle of Bunker Hill - First British
Attack
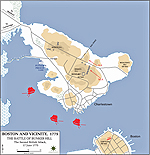
Bunker Hill - Second British Attack
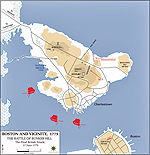
Battle of Bunker Hill - Final British
Attack
|
|
1775,
December 31 |
 Battle of Quebec Battle of Quebec
|
|
1776,
February 27 |
Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge, North Carolina, American victory
|
|
1776, August 27 |
Battle of Long Island, New York, British victory
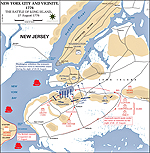
Map of the Battle of Long Island
|
|
1776, September 16 |
Battle of Harlem Heights, New York, American victory
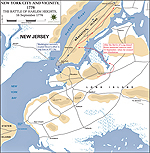
Map of the Battle of Harlem Heights
|
|
1776, October 11 |
Battle of Valcour Island, New York, Draw
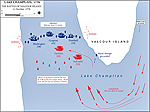
Map of the Battle of Valcour Island
|
|
1776, October 28 |
Battle of White Plains, New York, Draw
|
|
1776, November 16 |
Battle of Fort Washington, New York, British victory
|
|
1776, December 26 |
Battle of Trenton, New Jersey, American victory
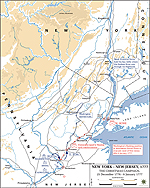
Map of the Christmas Campaign
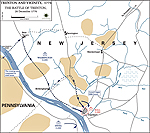
Map of the Battle of Trenton
|
|
1777, January 3 |
Battle of Princeton, New Jersey, American victory
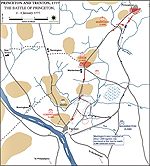
Map of the Battle of Princeton
|
|
1777, June 21 - October 17
|
 Saratoga Campaign Saratoga Campaign
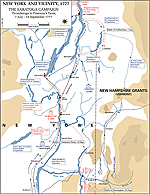
Saratoga Campaign 1777
|
|
1777, July 6 |
Battle of
Ticonderoga, northeastern New York, capture of Fort
Ticonderoga by the British
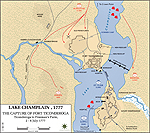
Map of the Battle of Ticonderoga
|
|
1777, August 6
|
Battle of
Oriskany (Battle of Oriska),
Oriskany Creek, one of the bloodiest battles
of the American Revolution
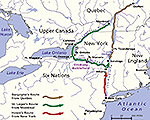
Map of the Oriskany
Battlefield
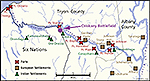
Mohawk River Valley
|
|
1777, August 16
|
Battle of
Bennington, Vermont, today's
Walloomsac, New York
Colonists, led by John Stark,
defeat the British, led by Friedrich Baum.
|
|
1777, September 11 |
Battle of
the Brandywine, Brandywine Creek, Pennsylvania, British victory

Map of the Battle of the Brandywine

Map 2 of the Battle of the Brandywine
|
|
1777, September 19 |
 First Battle of Saratoga,
also called: First Battle of Freeman's Farm, New York, American victory First Battle of Saratoga,
also called: First Battle of Freeman's Farm, New York, American victory
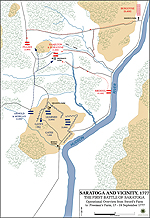
Map of the First Battle of Saratoga - Operations September
17-19, 1777
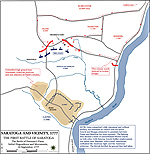
First Battle of Saratoga -
Initial Dispositions
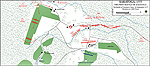
First Battle of Saratoga:
Battle Situation at 1300 Hours
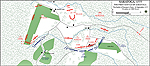
First Battle of Saratoga:
Battle Situation at 1500 Hours
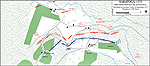
First Battle of Saratoga:
Battle Situation at 1700 Hours
|
|
1777, October 4 |
Battle of Germantown, Pennsylvania, British victory
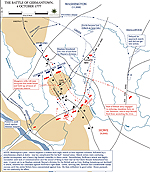
Map of the Battle of Germantown
|
|
1777, October 6 |
Battles of Fort Montgomery and
Fort Clinton, west side of the Hudson River, British
attack and victory led by General Henry Clinton
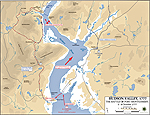
Map of the Battles of Fort Montgomery and Fort Clinton:
Prelude
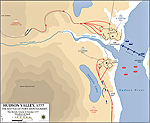
Map of the Battles of Fort Montgomery and Fort Clinton
|
|
1777, October 7 |
 Second Battle of
Saratoga Second Battle of
Saratoga
also called Second Battle of Freeman's
Farm or the Battle of Bemis Heights, New York, American victory
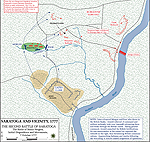
Map of the Second Battle of Saratoga: Initial Dispositions
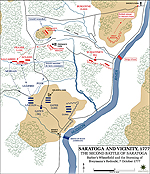
Map of the Second Battle of Saratoga
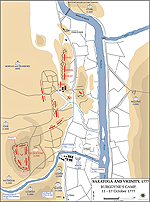
Burgoyne's Camp - October 11-17, 1777
|
|
1778, June 28 |
Battle of Monmouth, also called
Battle of Monmouth Court House, Monmouth, New Jersey, Draw
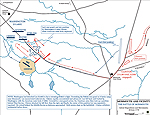
Map of the Battle of Monmouth
And speaking about help in the trenches...
Molly Pitcher
might or might not have been the lady people today would
love to believe. If she was, her real name was Mary Hays,
married to William Hays, who fought in this battle. Mary
might have been the good soul who carried water to the
soldiers and maybe even shot at the enemy herself when her
husband was wounded.
|
|
1779, July 16 |
Battle of Stony Point,
Stony Point, New York, American victory
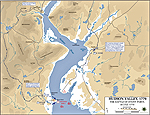
Map of the Battle of Stony Point
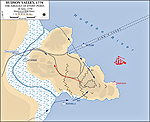
Map of the Battle of Stony Point: Attack
|
|
1780, April 1-May 12 |
Siege of Charleston, South Carolina
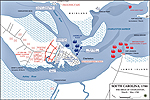
1780 Siege of Charleston
|
|
1780, August 16 |
Battle of Camden, South Carolina, British victory
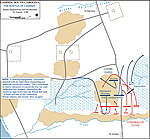
Map of the Battle of Camden
|
|
1780, October 7 |
Battle of Kings Mountain, South Carolina, American victory
|
|
1781, January 17 |
Battle of Cowpens, South Carolina, American victory
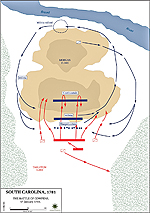
Map of the Battle of Cowpens
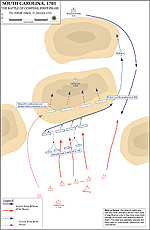
Battle of Cowpens: British Attack
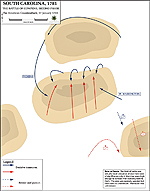
Battle of Cowpens: American Counterattack
|
|
1781, March 9 - May 10 |
 Siege of Pensacola,
British West Florida, Spanish victory
Siege of Pensacola,
British West Florida, Spanish victory |
|
1781, March 15 |
Battle of Guilford Courthouse, North Carolina, British victory
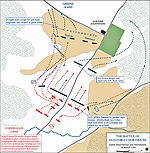
Battle of Guilford Courthouse
|
|
1781, September 5 |
Battle of Virginia Capes,
near Chesapeake Bay, naval battle, American (French) victory
|
|
1781, September 8 |
Battle of Eutaw Springs,
South Carolina
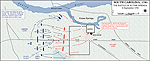
Map of the Battle of Eutaw Springs
|
|
1781, September 28 - October 19 |
Siege of Yorktown, Virginia, American victory
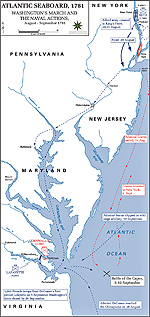
March to Yorktown,
August-September 1781
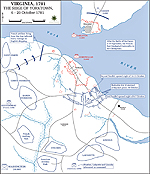
Siege of Yorktown
|
Timelines of the
American Revolution
 Timeline of the American Revolution (USMA)
Timeline of the American Revolution (USMA)
 Timeline of the American Revolution (EK)
Timeline of the American Revolution (EK)
The American
Revolution and the Native Americans
Thayendanegea, aka
Joseph Brant, was a
notable Native American who fought in the American
Revolution. A Mohawk Indian chief, he became a Christian
missionary as well as a British military officer. This made
sense because his sister Molly
was married to Sir William Johnson,
the British superintendent for northern Indian affairs.
The American
Revolution and the Spanish
Spain decided the American Revolution was a good opportunity
to take back Gibraltar from the British, who had occupied
The Rock since 1704 (see
 War of the Spanish Succession).
War of the Spanish Succession).
On June 21, 1779, Spain declared war on Britain and
commenced the
Great Siege of Gibraltar.
More than three years later, on February 3, 1783, the Great
Siege ended. Britain kept Gibraltar (see
 Treaty of Versailles of 1783).
Treaty of Versailles of 1783).
The American
Revolution and the Dutch
Britain didn't appreciate the trade that went on between the
Americans and the Dutch, so they declared war on the United
Provinces on December 20, 1780, thus starting the
 Fourth
Anglo-Dutch War (1780-1784). Fourth
Anglo-Dutch War (1780-1784).
Peace was officially restored with the
 Treaty of Paris of 1784.
Treaty of Paris of 1784.
The American
Revolution and the French
French support was especially crucial to
the American victory. Inspired by the American Revolution, the
French started their own revolution shortly after.
See more
under
 French Revolution. French Revolution.
Regarding French aid to the Americans, see also
 Vergennes.
Vergennes.
And the 1783 peace treaty between Great Britain and France was the
Treaty of Versailles.
See also what is sometimes called America's Second War of
Independence, the
 War of 1812.
War of 1812.
And maybe, the
 American Timeline.
American Timeline.
More History
|