Reference Maps on World War I — 1914-1918
Map of the Western Front in 1914
Map of the Eastern Front in 1914
Map of the Ottoman Empire 1914
Map of the Serbian Campaign - August-December 1914
Map of Northwest Europe: Opposing Armies - August 2, 1914
Map of the Battle of the Frontiers (North: Belgium and France) - August 1914
Map of the Battle of the Frontiers (South: Eastern France) - August 1914
Map of the Tannenberg Campaign 1914 - Movements August 17-23, 1914
Map of Belgium - August 20, 1914
Map of Northwest Europe - August 26-30, 1914: Allied Retreat
Map of the Battle of Tannenberg - August 26, 1914 (Part 1)
Map of the Battle of Tannenberg - August27-30, 1914 (Part 2)
Map of Northwest Europe - August 30-September 5, 1914: Allied Retreat
Map of the First Battle of the Marne - September 6-12, 1914
Map of the Eastern Front - Sept 28-Nov 1, 1914: Campaign in Southwest Poland
Map of the Western Front: Sept 30-Nov 11, 1914
Map of Mesopotamia 1914 - Anglo-Indian Invasion
Map of the Western Front 1915-1916
Map of Mesopotamia - January-July 1915
Map of the Battle of the Masurian Lakes - Feb 7-22, 1915
Map of the Dardanelles and Gallipoli Peninsula - Feb-Apr 1915
Map of the Eastern Front - May 1-Sept 30, 1915: German Breakthrough in the Gorlice-Tarnów Area
Map of the Battles of the Isonzo - 1915-1917
Map of Mesopotamia July-November 1915
Map of Serbia and the Salonika Expedition - October 7, 1915
Map of the Battle of Verdun - Feb 21-Dec 18, 1916
Map of the Eastern Front - March 1916 - Prior to the Brusilov Breakthrough against Austria-Hungary June-August 1916
Map of the Eastern Front - May-Sept 1916 - the Brusilov Offensive
Map of the Battle of Jutland - May 31-June 1, 1916
Map of the First Battle of the Somme - Jul 1-Nov 13, 1916
Map of the Romanian Campaign - Aug 27-Sep 18, 1916
Map of the Romanian Campaign - Sep 19-Oct 25, 1916
Map of the Romanian Campaign - Nov 26, 1916-Jan 7, 1917
Map of the Eastern Front 1917-8
Map of the First Battle of Gaza - March 26, 1917
Map of the Baltic Islands - Oct 10-20, 1917
Map of the Battle of Caporetto - Oct 24-Nov 19, 1917
Map of the Third Battle of Gaza - Oct 31-Nov 7, 1917
Map of the Western Front 1918 - Five German Offensives
Map of the Battle of Megiddo - Sep 19-21, 1918
Map of the Western Front - Sept 25-Nov 11, 1918 - Final Allied Offensive
Map of the Battles of the Meuse-Argonne - Sept 26-Nov 11, 1918
Map of the Battle of Vittorio Veneto - Oct 24-Nov 3, 1918
Map of the Territorial Losses of World War One
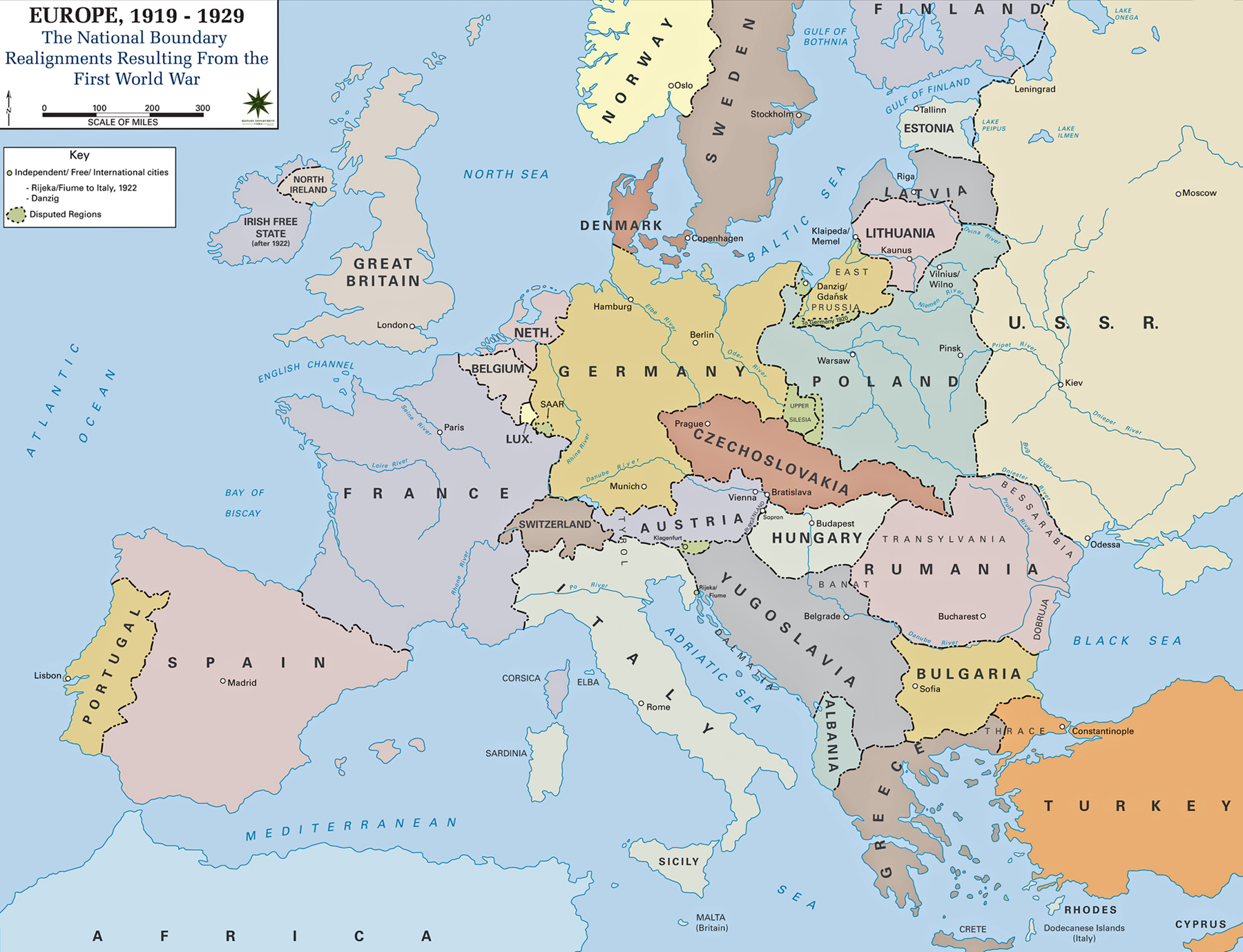
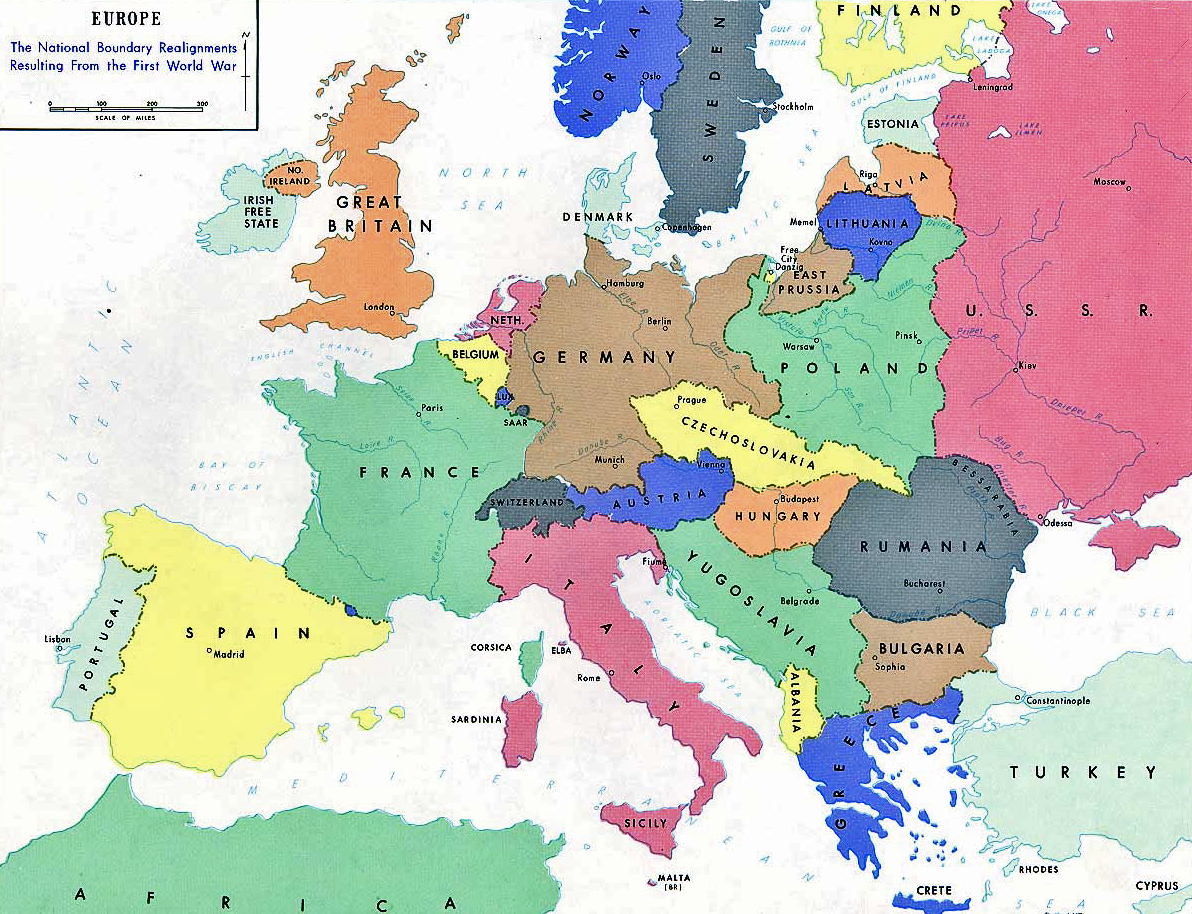
Map of Europe in 1919: the national boundary realignments resulting from the First World War
Map of the World in 1919: Political Realignment Following the First World War