|

 Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
 Musicians, Painters &
Artists
Musicians, Painters &
Artists
 Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
 Native Americans & The Wild
West
Native Americans & The Wild
West
 First Ladies
First Ladies
 Popes
Popes
 Troublemakers
Troublemakers
 Historians
Historians
 Archaeologists
Archaeologists
 Royal Families
Royal Families
 Tribes & Peoples
Tribes & Peoples

Assassinations in History
Who
got slain, almost slain, when, how,
why, and by whom?
 Go to the
Assassination Archive
Go to the
Assassination Archive




Online History Dictionary A - Z
All-Time Records in
History
What was the
bloodiest battle, the battle with the least
casualties, who was the greatest military leader?
 Go to
Records in History
Go to
Records in History

Faces of World War I
 Francis Ferdinand
Francis Ferdinand
 Francis Joseph
Francis Joseph
 William II
William II
 Alfred Schlieffen
Alfred Schlieffen
 T.E. Lawrence
T.E. Lawrence
 Georges Clemenceau
Georges Clemenceau
 David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George
 Arthur Zimmermann
Arthur Zimmermann
 Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
World War I Timelines
 World War I -
1914
World War I -
1914
 World
War I - 1915
World
War I - 1915
 World
War I - 1916
World
War I - 1916
 World
War I - 1917
World
War I - 1917
 World
War I - 1918
World
War I - 1918
 World War I in the
Stream of Time
World War I in the
Stream of Time
 Who All Watched WWI?
Who All Watched WWI?
World War I Documents
 Treaty of Versailles
1919
Treaty of Versailles
1919
 Treaty of Saint
Germain 1919
Treaty of Saint
Germain 1919
World War I Maps
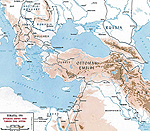
MAP OF THE OTTOMAN
EMPIRE 1914
Click map to enlarge
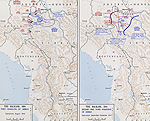
MAP OF THE SERBIAN
CAMPAIGN
August-December 1914
Click map to enlarge
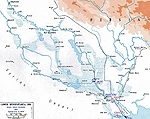
MAP OF MESOPOTAMIA
1914 -
ANGLO-INDIAN INVASION
Click map to enlarge
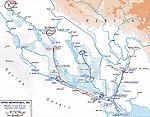
MAP OF MESOPOTAMIA -
January-July 1915
Click map to enlarge
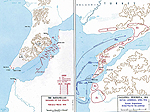
MAP OF THE DARDANELLES
AND
GALLIPOLI PENINSULA - Feb-Apr 1915
Click map to enlarge
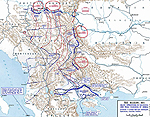
MAP OF SERBIA AND THE
SALONIKA EXPEDITION - October 7, 1915
Click map to enlarge
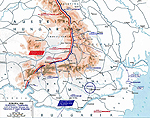
MAP OF THE ROMANIAN
CAMPAIGN -
Aug 27-Sep 18, 1916
Click map to enlarge
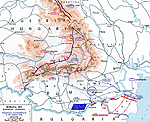
MAP OF THE ROMANIAN
CAMPAIGN -
Sep 19-Oct 25, 1916
Click map to enlarge
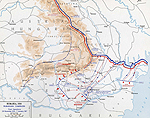
MAP OF THE ROMANIAN
CAMPAIGN -
Nov 26, 1916-Jan 7, 1917
Click map to enlarge
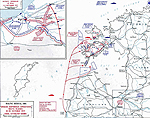
MAP OF THE BALTIC
ISLANDS - Oct 10-20, 1917
Click map to enlarge
The Western Front
Maps capturing the events on the
Western Front
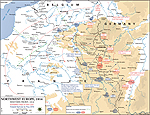
MAP OF THE WESTERN
FRONT 1914
Click map to enlarge
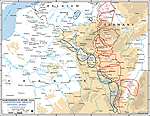
MAP OF NORTHWEST EUROPE: CONCENTRATION OF
OPPOSING ARMIES - August 2, 1914
Click map to enlarge
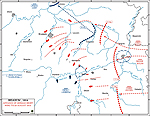
MAP OF BELGIUM:
ADVANCE OF
THE GERMAN RIGHT WING - August 20, 1914
Click map to enlarge
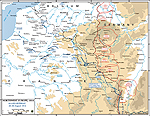
MAP OF THE ALLIED
RETREAT -
August 26-30, 1914
Click map to enlarge
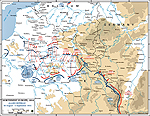
MAP OF THE ALLIED
RETREAT -
August 30-September 5, 1914
Click map to enlarge
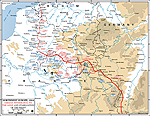
MAP OF THE WESTERN
FRONT -
Sept 30-Nov 11, 1914
Click map to enlarge
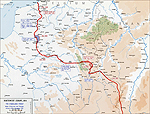
MAP OF THE WESTERN
FRONT 1915-1916
Click map to enlarge
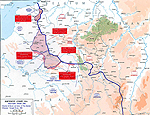
MAP OF THE WESTERN
FRONT 1918:
FIVE GERMAN OFFENSIVES
Click map to enlarge
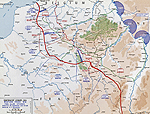
MAP OF THE WESTERN
FRONT: FINAL ALLIED OFFENSIVE - Sept 25-Nov 11, 1918
Click map to enlarge
The Eastern Front
Maps illustrating the battles and
events on the Eastern Front
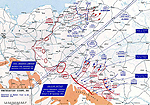
MAP OF THE EASTERN
FRONT 1914
Click map to enlarge
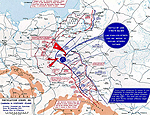
MAP OF THE EASTERN
FRONT:
CAMPAIGN IN SOUTHWEST POLAND -
Sept 28-Nov 1, 1914
Click map to enlarge
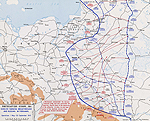
MAP OF THE EASTERN
FRONT: GERMAN BREAKTHROUGH
IN THE GORLICE-TARNOW AREA - May 1-Sept 30, 1915
Click map to enlarge
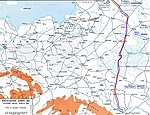
MAP OF THE EASTERN FRONT - March 1916
Click map to enlarge
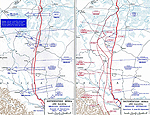
MAP OF THE EASTERN
FRONT: THE BRUSILOV OFFENSIVE - May-Sept 1916
Click map to enlarge
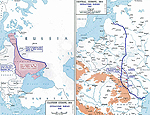
MAP OF THE EASTERN
FRONT 1917-8
Click map to enlarge
|
|

WORLD WAR ONE
1914 - 1918
The Sarajevo
Ripple Effect
Prior to
 World War II, World War I was called
The Great War.
World War II, World War I was called
The Great War.
|
|
Over 65 million troops were engaged in the First World War, an
unprecedented number in 1914.
Consequently, the war also set a sad
record in wreaking havoc.
For the most part, the war was fought in
Europe; however, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia saw action as
well.
Who was involved in World War I?
In one way or another, almost everybody. Only the following countries managed to remain
neutral:
In Europe: Denmark, Holland,
Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, and Spain.
In the Americas: Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and
Venezuela.
In Asia: Afghanistan and Persia.
In Africa: Abyssinia.
The main combatants of
WWI
The Central Powers fought against the Allies.
The Central Powers were Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey and
Bulgaria.
|
The Allies
were France, Great Britain,
Russia, Italy, Japan, United States, Romania, Serbia, Belgium,
Greece, Portugal, and Montenegro.
And here they are on a map.
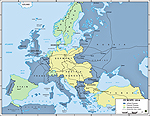
Europe 1914 - Allied, Central, and Neutral
Powers
What were the causes
of World War I?
Imperialistic expansion was backed by
a widespread net of military alliances. This extensive alliance
system was vulnerable, since nothing could happen without everyone's
being affected.
In simpler terms,
everybody made a promise to everybody to help them out in case they
got attacked. Now, all that needed to happen was someone had to
sneeze and everybody would be forced to take sides and fight whether
they wanted to or not.
In fact, someone did sneeze on June 28,
1914.
What started World War I?
On June 28, 1914, Serbian radical
Gavrilo Princip assassinated
 Archduke Franz-Ferdinand of Austria
in Sarajevo. A month later, on July 28, 1914, Austria declared
war against Serbia and the rest of the globe followed
into World War I.
Archduke Franz-Ferdinand of Austria
in Sarajevo. A month later, on July 28, 1914, Austria declared
war against Serbia and the rest of the globe followed
into World War I.
What ended World War I?
Bulgaria surrendered on
September 30, 1918; Turkey on October 30; and Austria-Hungary on
November 4, 1918.
On November 11, 1918, an armistice was signed
between the Allies and Germany. World War I was officially ended.

The peace conference was headed by the
"Big Four,"
 David Lloyd George of Britain,
David Lloyd George of Britain,
 Georges Clemenceau of
France,
Georges Clemenceau of
France,
Vittorio Orlando of Italy, and
 Woodrow Wilson of the United
States.
Woodrow Wilson of the United
States.
Who won World War I?
Who lost World War I?
The Allies were the victors of World
War I. The Central Powers lost World War I.
What were the
casualties of World War I?
During the four years of war, more
than 8.5 million soldiers were killed and 20 million wounded. A
total of 15,000,000 million deaths are estimated. Roughly 90% of all
Austrian mobilized forces became casualties.
 Check the American war
casualties report
Check the American war
casualties report
Treaties of World War
I
At the end of WWI, the Allies concluded the  Treaty
of Versailles with Germany and the
Treaty
of Versailles with Germany and the  Treaty of Saint Germain with Austria.
Treaty of Saint Germain with Austria.
And this is what everybody lost / gained
on the European map:
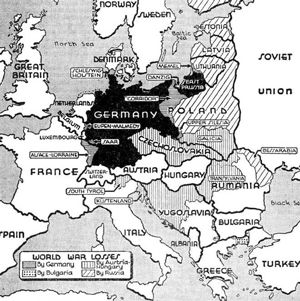
GERMANY BEFORE AND AFTER
THE TREATY OF VERSAILLES
Click to enlarge
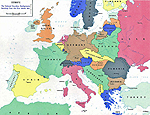
Europe 1919:
the national boundary realignments
resulting from the First World War
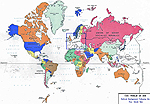
1919 World Map:
Political Realignment
Following the First World War
The United States and
World War I
The United States was determined to
remain neutral in European affairs. However, Germany’s
unrestricted submarine warfare
soon changed America’s opinion.
Furthermore, the
Zimmermann Telegram was intercepted by the United
States. This telegram, sent by  Arthur Zimmermann, revealed
Germany’s proposal of an alliance with Mexico against the United
States, and "an understanding on our [the German's] part that Mexico
is to reconquer the lost territory in Texas, New Mexico, and
Arizona.”
Arthur Zimmermann, revealed
Germany’s proposal of an alliance with Mexico against the United
States, and "an understanding on our [the German's] part that Mexico
is to reconquer the lost territory in Texas, New Mexico, and
Arizona.”
The Americans rubbed their eyes twice, read the telegram again,
and on April 6, 1917, the United States entered World War I.
Russia and
World War I
Simultaneously, the Russians had their hands full with World War I and the  Russian Revolution of 1917
which turned everything in the country upside down. Russian Revolution of 1917
which turned everything in the country upside down.
And, without a
breather, the nation went on trying to survive the  Russian Civil War 1918-1920,
which turned out to have been a walk in the park compared to the
following chapter, the reign of mass murderer
Russian Civil War 1918-1920,
which turned out to have been a walk in the park compared to the
following chapter, the reign of mass murderer  Stalin from 1928-1953, whose colossal cruelty
was only interrupted by
Stalin from 1928-1953, whose colossal cruelty
was only interrupted by  World War II, during which
Russia lost 18 million of its people.
World War II, during which
Russia lost 18 million of its people.
This is the incredibly devastating
background of the Russian people.
The Impact of World War I on
Humankind
The First World War ended four
dynastic empires in the country of
- Germany ( Hohenzollern Dynasty)
Hohenzollern Dynasty)
- Russia ( Romanov Dynasty)
Romanov Dynasty)
- Austria-Hungary ( Habsburg Dynasty)
Habsburg Dynasty)
- Turkey (Ottoman
Dynasty)
For names of
the last emperors and their successors see
the
 Lvov Trivia.
Lvov Trivia.
The war also
drastically reshaped the map of Europe, leaving
much of it in economic desperation.
All of
Germany's overseas colonies in China, in the
Pacific, and in Africa were taken over by the
Allies.
The Battles of World
War I
|
August
14 - September 5, 1914 |
 Battle of the Frontiers
Battle of the Frontiers |
|
|
|
|
August 20-22,
1914 |
 Battle of
Morhange-Sarrebourg, part of the
Battle of
Morhange-Sarrebourg, part of the
 Battle of the Frontiers
Battle of the Frontiers |
|
|
|
|
August 26-30,
1914 |
 Battle of Tannenberg
Battle of Tannenberg
|
|
|
|
|
September 6-12,
1914 |
 First Battle of the Marne
First Battle of the Marne
|
|
|
|
|
September 9-14,
1914 |
 First Battle of the Masurian Lakes
First Battle of the Masurian Lakes
|
|
|
|
|
October 12-November 11, 1914 |
 First Battle of Ypres
First Battle of Ypres
|
|
|
|
|
November 11-December 6,
1914 |
 Battle of Lodz
Battle of Lodz |
|
|
|
|
February 7-22,
1915 |
 Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes,
also called Winter Battle of the Masurian Lakes or
Winter
Battle of Masuria
Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes,
also called Winter Battle of the Masurian Lakes or
Winter
Battle of Masuria
|
|
|
|
|
February 19, 1915 -January 1916 |
 Dardanelles Campaign, also
called Gallipoli Campaign
Dardanelles Campaign, also
called Gallipoli Campaign |
|
|
|
|
April 22-May 25,
1915 |
 Second Battle of Ypres
Second Battle of Ypres |
|
|
|
|
June 23-July 7, 1915 |
 First Battle of the Isonzo
First Battle of the Isonzo
|
|
|
|
|
July 18-August 3, 1915 |
 Second Battle of the Isonzo
Second Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
September 25 - October 13, 1915 |
 Battle of Loos
Battle of Loos
|
|
|
|
|
September 28, 1915 |
 First Battle of Kut (Al-Kut)
First Battle of Kut (Al-Kut)
|
|
|
|
|
October 18-November 3, 1915 |
 Third Battle of the Isonzo
Third Battle of the Isonzo
|
|
|
|
|
November 10-December 2,
1915 |
 Fourth Battle of the Isonzo
Fourth Battle of the Isonzo
|
|
|
|
|
February 21-December 15, 1916 |
 Battle of Verdun
Battle of Verdun
|
|
|
|
|
March 9-17,
1916 |
 Fifth Battle of the Isonzo
Fifth Battle of the Isonzo
|
|
|
|
|
May 31-June 1, 1916 |
 Battle of Jutland, also called
Battle of the Skagerrak
Battle of Jutland, also called
Battle of the Skagerrak
|
|
|
|
|
July 1-November 13, 1916 |
 First Battle of the Somme
First Battle of the Somme
|
|
|
|
|
August 6-17,
1916 |
 Sixth Battle of the Isonzo
Sixth Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
September 14-17, 1916 |
 Seventh Battle of the Isonzo
Seventh Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
October 10-12, 1916 |
 Eighth Battle of the Isonzo
Eighth Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
November 1-4, 1916 |
 Ninth Battle of the Isonzo
Ninth Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
February 22-23, 1917 |
 Second Battle of Kut (Al-Kut)
Second Battle of Kut (Al-Kut)
|
|
|
|
|
March 26, 1917 |
 First Battle of Gaza
First Battle of Gaza
|
|
|
|
|
April 19, 1917 |
 Second Battle of Gaza
Second Battle of Gaza |
|
|
|
|
May 12-June 8, 1917 |
 Tenth Battle of the Isonzo
Tenth Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
July 31-November 6, 1917 |
 Third Battle of Ypres, also
called the Battle of Passchendaele
Third Battle of Ypres, also
called the Battle of Passchendaele
|
|
|
|
|
August 19-September 12,
1917 |
 Eleventh Battle of the Isonzo
Eleventh Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
October 24-November 19,
1917 |
 Battle of Caporetto, also called
Twelfth Battle of the Isonzo
Battle of Caporetto, also called
Twelfth Battle of the Isonzo |
|
|
|
|
October 31-November 7, 1917 |
 Third Battle of Gaza
Third Battle of Gaza
|
|
|
|
|
November 20 - December 7, 1917 |
 Battle of Cambrai
Battle of Cambrai
|
|
|
|
|
March 21-April 5, 1918 |
 Second Battle of the Somme
also called
Battle of Saint-Quentin
Second Battle of the Somme
also called
Battle of Saint-Quentin |
|
|
|
|
July 15-18, 1918 |
 Second Battle of the Marne
Second Battle of the Marne |
|
|
|
|
August
8 - 12, 1918 |
 Battle of Amiens
Battle of Amiens
|
|
|
|
|
September 19-21,
1918 |
 Battle of Megiddo
Battle of Megiddo
|
|
|
|
|
September 26-November 11, 1918 |
 Battles of the Meuse-Argonne
Battles of the Meuse-Argonne
|
|
|
|
|
October 24-November 3, 1918 |
 Battle of Vittorio Veneto
Battle of Vittorio Veneto |
|
|
|
Go here for the
 Timelines of World War One
Timelines of World War One
Armenian Genocide
During the war, the government of the
Ottoman Empire (Turkey) instigated the
Armenian Genocide. The genocide lasted from 1915 until
1923, caused 1.5 million deaths, and even to this day has gone
relatively unnoticed.
In fact, until this day the Armenian
Genocide remains a hot topic.
Some Armenians are of the opinion that Turkey can't really become
part of Europe until it acknowledges its part played in the Armenian
Genocide. Apparently, a certain Mr Hrant Dink was of this opinion as
well. He was a Turkish citizen of Armenian descent and was
assassinated in front of his office on January 19, 2007. Mr Dink was
a newspaper editor. The Turkish government brought 18 people to
trial for this assassination.
More from the
 Washington Post...
Washington Post...
Encyclopaedia Britannica tell us
The Armenians
are traditionally members of either the
Monophysite Armenian Apostolic (Orthodox)
church or the Armenian Catholic branch of
the Roman Catholic church.
The population of
Turkey are predominantly Muslims.
The Armenian Genocide proved inspirational for
Nut Adolf.
"Who, after all, speaks today of the
annihilation of the Armenians?"
More about
Hitler's quote from the
 Armenian National
Institute.
Armenian National
Institute.
World War I
Controversy
Which persons or nations were most
responsible for the war’s outbreak is debated.
World War I Trivia
Compared to previous wars,
technological advances heavily increased the casualties of World War
I. Tank, submarine, and airplane warfare was introduced as well as
the machine gun and poison gas.
World War I became infamous for its costly trench warfare at the
Western Front which stretched
from the North Sea to the Swiss border.
Here you can
 Check the
costs of major US wars in comparison.
Check the
costs of major US wars in comparison.
Read up on the brief but intense
 war experience of one Stanley C. Griffin.
war experience of one Stanley C. Griffin.
Here is more on
 Mata Hari.
Mata Hari.

And here is a fabulous photograph from Zooniverse. If you are a
citizen historian and you can spare a moment, take part in this
impressive project,
 Operation War Diary.
Operation War Diary.

Happy World War I Soldiers
Click to enlarge
At eleven o'clock this morning came to an end
the cruelest and most terrible war that has ever scourged mankind. I
hope we may say that thus, this fateful morning, came to and end all
wars.
David Lloyd George, November 11, 1918
See also
 American Timeline.
American Timeline.
Maybe, see also
 Human Rights
Human Rights
More History
|