|
Second Punic War 218-201 BC
 What does
Punic even mean?
What does
Punic even mean?
Who Won the Second
Punic War?
Rome won the Second Punic War.
Why Was the Second
Punic War Fought?
Carthage was a wealthy trading city,
and its leaders were flirting with
the idea of controlling Spain and
Sicily, while Rome very much liked
the idea of expanding as well and
controlling North Africa while at
it.
Here
is the situation on a map
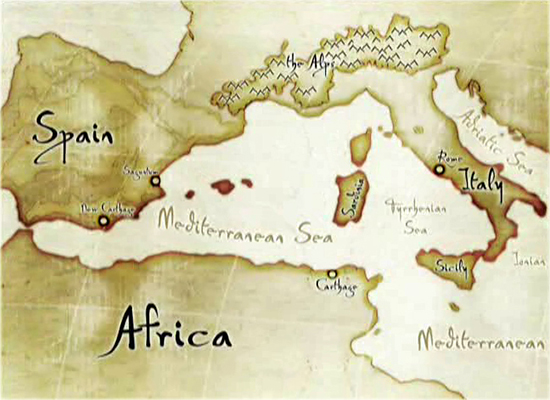
Map Illustrating Desired Control of
the Mediterranean Sea
Rome vs. Carthage
History Channel
In
addition, the outcome of the
 First Punic
War (Carthage had
lost its Sicilian strongholds and
had to make out annual pay checks to
Rome) did not sit well with
Carthage.
First Punic
War (Carthage had
lost its Sicilian strongholds and
had to make out annual pay checks to
Rome) did not sit well with
Carthage.
Carthage recovered, reorganized, and
was ready to reshuffle. New Carthaginian
strongholds in Spain and a large
Carthaginian army became a worry for
Rome. Rome was ready for war in order to
eliminate the growing threat.
Choosing a Battlefield
Hannibal decided that the
best strategy of defense was to
attack the enemy right at its
center.
Thus, in 218 BC he began his
march north through Spain with an
army of 100,000 men and 37 elephants.
War elephants, by the way, were so
important that they were portrayed
on coins.

Silver Double Shekel of Carthage
Diameter: 25 mm. Issued by
Hannibal's family in Spain. From the
Mogente Hoard, Valencia, Spain,
around 230 BC. The Punic
(Carthaginian) god Melqart is shown
on the front of the coin. He is
depicted resembling the Greek hero
Herakles with a club over his
shoulder. On the reverse is a war
elephant, as used by Hannibal in his
great campaign against Rome.
The
British Museum
And just in case you were wondering
how long 25 millimeters really are,
here is your clue:
Back
to the Second Punic War.
So, instead of crossing the Mediterranean Sea, they went the
other way around, through Spain, across the Pyrenees, crossing the Rhône
River, crossing the Alps, and crushing Turin on the way.
Here
is Hannibal's Route of Invasion:
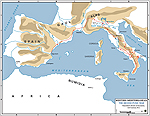
Map of Hannibal's Invasion Route 218 BC
Only one elephant survived the long
trip and Roman
general
 Publius Cornelius Scipio was ready to have it for
breakfast.
Publius Cornelius Scipio was ready to have it for
breakfast.
But Hannibal won one battle after another.
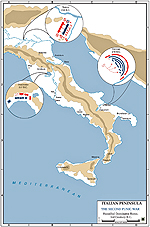
Map of the Battles of the Second Punic War 218-201 BC
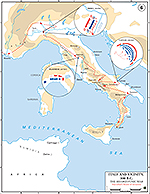
Second Punic War 218 – 201 BC:
Hannibal's Route of Invasion
The Battles of the Second Punic War
The major battles of the Second Punic
War were
218 BC
Battle of the
Trebia
217 BC
Battle of Trasimene
216 BC
 Battle of Cannae
Battle of Cannae
207 BC
 Battle of the
Metaurus
Battle of the
Metaurus
206 BC Battle of Ilipa
202 BC Battle of Zama
The Events of the Second Punic War in a Nutshell
In December 218 BC, Hannibal defeated
the Romans at the Battle of the
Trebia. Battle location was the left bank of the Trebia
River south of Placentia. Today, it's the Trebbia River and
Piacenza. Hannibal faced Scipio and Tiberius Sempronius Longus.
The Romans lost half of their army.
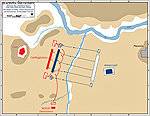
Map of the Battle of the Trebia 218 BC
In 217 BC, Hannibal ambushed the Roman
army at the Battle of Trasimene,
which was more a massacre than a battle. At least 15,000 Roman
troops were killed.
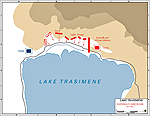
Map of the Battle of Lake Trasimene 217 BC
In 216 BC, at the
Battle of Cannae,
which is today's Monte di Canne, Hannibal sent the Romans packing once
again.
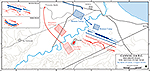
216 BC Battle of
Cannae - Phase One, Two, and Three

Map of the Battle of Cannae 216 BC - Initial Attack
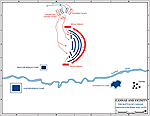
Map of the Battle of Cannae 216 BC - Final Attack
Here is more about the
 Battle of Cannae.
Battle of Cannae.
Unfortunately for Hannibal, it went slowly downhill from
there. Little by little, the Romans re-captured their cities.
In 205 BC, the smart man Scipio was elected consul and decided
to bring war to Hannibal's home continent Africa. He gained several
victories there, the Carthaginians panicked and recalled Hannibal from Italy to
defend the fatherland. Hannibal complied and the Italians could breathe
a sigh of relief.
In 202 BC, the final battle of the
Second Punic War followed, the Battle of Zama. Scipio and the
Romans won. Hannibal was defeated, Carthage had to sue for peace.
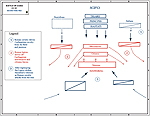
Map of the Battle of Zama 202 BC
In 201 BC, Scipio was officially re-named Publius Cornelius
Scipio Africanus, and he sure earned it.
At the end
of the Second Punic War, Rome was confirmed in the dominion of Italy,
Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica, dominant throughout a great
part of Spain, and virtually predominant in North Africa.
Check the maps:
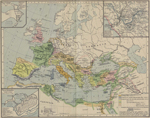
Map of Rome's Expansion 264-180 BC
Click to enlarge
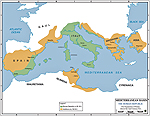
2nd Century Expansion
of the Roman Republic
Go to:
 First
Punic War
First
Punic War
 Third
Punic War
Third
Punic War
See all
 Punic Wars.
Punic Wars.
More History
|