|

 Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
Explorers, Scientists &
Inventors
 Musicians, Painters &
Artists
Musicians, Painters &
Artists
 Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
Poets, Writers &
Philosophers
 Native Americans & The Wild
West
Native Americans & The Wild
West
 First Ladies
First Ladies
 Popes
Popes
 Troublemakers
Troublemakers
 Historians
Historians
 Archaeologists
Archaeologists
 Royal Families
Royal Families
 Tribes & Peoples
Tribes & Peoples

Assassinations in History
Who
got slain, almost slain, when, how,
why, and by whom?
 Go to the
Assassination Archive
Go to the
Assassination Archive




Online History Dictionary A - Z
All-Time Records in
History
What was the
bloodiest battle, the battle with the least
casualties, who was the greatest military leader?
 Go to
Records in History
Go to
Records in History

Who Really Benefits from Revolutions?
I am a little
reconciled to the theatre.
[...] and as all the properties have changed
masters, the actresses have no end of diamonds.
Metternich at
Rastatt, Memoirs,
December 12, 1797
|
|

La Marseillaise — French
National Anthem, Composed in 1792
French Revolutionary Wars 1792-1802
|
|
Why Were the French Revolutionary Wars Fought?
The French Revolution had introduced
liberal thoughts regarding equality, rights, and liberty.
The
French
Revolutionary Wars were fought in order to spread, or to
prevent the spreading of, the spirit, the ideas, and the
achievements of the
 French Revolution.
French Revolution.
When Did the French Revolutionary Wars Begin?
The French Revolutionary Wars started
when France declared war
on Austria on April 20, 1792.
In fact, this was the beginning of the
 War of the First Coalition, the
first phase of the French Revolutionary Wars.
War of the First Coalition, the
first phase of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Check this event in the
 timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Image Above
La Marseillaise, Lithograph
Musée des Civilisations de l'Europe et
de la Méditerranée / Iconothèque MNATP |
La Marseillaise is the French
national anthem, composed in just one night during the French
Revolution, on April 24, 1792, by
Claude-Joseph Rouget de Lisle.
At the time, De
Lisle was an army officer stationed at
Strasbourg. He composed both, lyrics and tune.
The original title of the song was Chant de
guerre de l'armée du Rhin, in other words,
War Song of the Army of the Rhine. It became
the Marseillaise when volunteers from Marseille
couldn't stop humming it.
What Ended the French Revolutionary Wars?
The French Revolutionary Wars ended
with the
 Treaty
of Amiens in March 1802, a peace treaty between
France and Britain. Treaty
of Amiens in March 1802, a peace treaty between
France and Britain.
Check this event in the
 Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Some mark February 1801 as the end of
the French Revolutionary Wars when the
 Peace of
Luneville was
signed. This was a peace treaty between France and her main enemy,
Austria. Peace of
Luneville was
signed. This was a peace treaty between France and her main enemy,
Austria.
Check this event in the
 Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
The Chapters of the
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars can be
divided into the following chapters:
The War of the First
Coalition
The
 War of the First Coalition
was fought
from 1792 to 1797.
War of the First Coalition
was fought
from 1792 to 1797.
Napoleon's First Italian Campaign was part of the War of the
First Coalition.
The Wars of the Vendee
The
 Wars of the Vendée
were fought from February 1793 to July 1796.
Wars of the Vendée
were fought from February 1793 to July 1796.
The Egyptian Campaign
Napoleon's Egypt Campaign
was in operation
from 1798 to 1801.
The War of the
Second Coalition
The
 War of the Second
Coalition was fought
from 1798 to 1802.
War of the Second
Coalition was fought
from 1798 to 1802.
Here is more
on the seven
 Coalitions
that were formed to fight against revolutionary France.
Coalitions
that were formed to fight against revolutionary France.
And here is France on a map with its 1789 and
1793 boundaries, along with the revolutionary
centers and the centers of counter-revolutionary
activity:
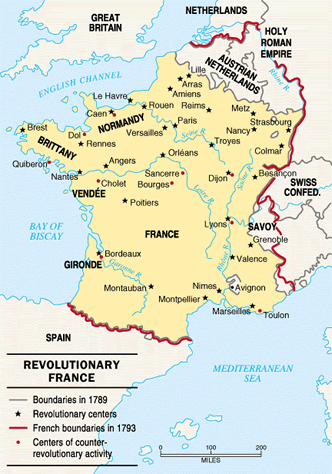
Map of Revolutionary France 1789 and 1793
The French Revolutionary Wars
and the French Sister Republics
By means of the French Revolutionary
Wars, France carried the French Revolution beyond French borders.
One of the methods to establish, and to keep, French revolutionary
thoughts alive outside of the French Republic, was to set up
so-called sister republics.
These sister republics were the
 Batavian
Republic - established on May 16, 1795
Batavian
Republic - established on May 16, 1795
Cispadane
Republic - established on December 30, 1796
(later part of the
 Cisalpine
Republic) Cisalpine
Republic)
 Ligurian
Republic - established on June 15, 1797
Ligurian
Republic - established on June 15, 1797
 Cisalpine
Republic - established on July 9, 1797
Cisalpine
Republic - established on July 9, 1797
 Roman Republic
- established on February 15, 1798
Roman Republic
- established on February 15, 1798
 Helvetic
Republic - established on March 29, 1798
Helvetic
Republic - established on March 29, 1798
 Parthenopean
Republic - established on January 24, 1799
Parthenopean
Republic - established on January 24, 1799
 Lucca Republic - established on
December 27, 1801
Lucca Republic - established on
December 27, 1801
French Revolutionary
Wars — Key Events
|
April 20, 1792 |
France declares war on Austria. |
| |
|
| |
This marks the beginning of the
 War of the
First Coalition. The
French Revolutionary Wars
begin.
War of the
First Coalition. The
French Revolutionary Wars
begin. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
April
29, 1792 |
France invades the Austrian
Netherlands. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
August
10, 1792 |
France is now a republic. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
September 20, 1792 |
 Battle of Valmy.
French victory. Battle of Valmy.
French victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
End of
November 1792 |
The French have occupied all of the
Austrian Netherlands / Belgium. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
January 21,
1793 |
Trial and execution of
 Louis XVI at Paris.
Louis XVI at Paris. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
February 1, 1793 |
France declares war on Great Britain
and the United Provinces. Europe is
now almost completely entangled in
the War of the First Coalition. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
February 20, 1793 |
The
 Wars of the
Vendee begin.
Wars of the
Vendee begin. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
March 1, 1793 |
Austrian counter-offensive begins.
 Battle of
Aldenhoven.
Austrian victory.
Battle of
Aldenhoven.
Austrian victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
August 23, 1793 |
The
 French
National Convention
orders a mass recruitment.
French
National Convention
orders a mass recruitment. |
| |
|
| |
|
| June 26, 1794 |
 Battle of Fleurus.
Important French victory. For
the next twenty years, France,
instead of Austria, will occupy
the Low Countries. Battle of Fleurus.
Important French victory. For
the next twenty years, France,
instead of Austria, will occupy
the Low Countries. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
April 5, 1795 |
 Peace
of Basel - Prussia accepts the Rhine River
as the French eastern border.
Peace
of Basel - Prussia accepts the Rhine River
as the French eastern border.
France won the
 War
of the First Coalition
against Prussia. One ally down,
four more to go. War
of the First Coalition
against Prussia. One ally down,
four more to go.
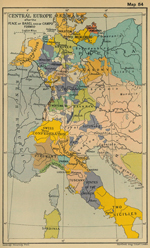
Central
Europe after the Peace of Basel (1795)
and of
Campo Formio (1797) |
| |
|
| |
|
|
May
16, 1795 |
 Batavian
Republic
proclaimed.
Batavian
Republic
proclaimed. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
June
27, 1795 |
 Battle of Quiberon Bay.
Victory for French
revolutionaries over French
royalists and their British
supporters. This battle was part
of the Battle of Quiberon Bay.
Victory for French
revolutionaries over French
royalists and their British
supporters. This battle was part
of the
 Wars of
the Vendee.
Wars of
the Vendee. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
March 2, 1796 |
Napoleon is appointed commander
in chief of the Army of Italy. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
July 1796 |
The
 Wars of the
Vendee end.
Wars of the
Vendee end. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
April
17, 1797 |
 Treaty
of Leoben.
This agreement was a draft of the
Treaty of Campo Formio (October
1797,) confirming French victory in
the War of the First Coalition. Treaty
of Leoben.
This agreement was a draft of the
Treaty of Campo Formio (October
1797,) confirming French victory in
the War of the First Coalition. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
September 4, 1797 |
Coup d'état of 18 Fructidor, year V.
Encouraged by Napoleon, the Directory
eliminates the royalists from the government. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
October 17, 1797 |
 Peace of Campo Formio.
France won the
Peace of Campo Formio.
France won the
 War
of the First Coalition. War
of the First Coalition.
Here is the map:

Central
Europe after the Peace of Basel (1795)
and of
Campo Formio (1797) |
| |
|
| |
The
 War
of the First Coalition
ends. War
of the First Coalition
ends. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
December 9, 1797 |
 Congress of Peace at Rastatt
Congress of Peace at Rastatt
(Rastatter Friedenskongress)
This congress formally
opened on January 19, 1798. It will last
until April 23, 1799. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
May 19, 1798 |
The
 Egyptian Campaign
begins.
Egyptian Campaign
begins. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
August 1, 1798 |
 Battle of the Nile
British victory over the French. This battle is part of
the
Battle of the Nile
British victory over the French. This battle is part of
the
 Egyptian Campaign.
Egyptian Campaign. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
September 11, 1798 |
The
 Ottoman Empire declares war on France.
Ottoman Empire declares war on France. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
November 29, 1798 |
Troops from Naples enter Rome and evict the
French. |
| |
|
| |
This
marks the beginning of the
 War
of the Second Coalition. War
of the Second Coalition. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
March 17-20, 1799 |
Abortive
 Siege of Acre by the
French. This battle is part of
the
Siege of Acre by the
French. This battle is part of
the
 Egyptian Campaign.
Egyptian Campaign. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
April 23, 1799 |
Congress of Peace at Rastatt
(Rastatter Friedenskongress) ends.
This congress had
commenced with its
first session on December 9, 1797. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
June 4-6, 1799 |
 First Battle of
Zurich.
Austrian victory. First Battle of
Zurich.
Austrian victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
September 25-26, 1799 |
 Second
Battle of Zurich.
French victory. Second
Battle of Zurich.
French victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
November 9, 1799 |
 Napoleon Bonaparte
comes to power via coup d'état (Coup
d'Etat du 18 Brumaire, year VIII) that
overthrows the
Napoleon Bonaparte
comes to power via coup d'état (Coup
d'Etat du 18 Brumaire, year VIII) that
overthrows the
 Directory
and installs the Directory
and installs the
 Consulate.
He is now First Consul of
France.
Consulate.
He is now First Consul of
France.
|
| |
This
marks the end of the
 French
Revolution.
French
Revolution. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
June 14, 1800 |
 Battle of Marengo.
French victory.
Battle of Marengo.
French victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
December 3, 1800 |
 Battle of Hohenlinden.
French victory.
Battle of Hohenlinden.
French victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
April 2, 1801 |
 Battle of Copenhagen.
British victory. Battle of Copenhagen.
British victory. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
February 9, 1801 |
 Peace of
Luneville.
France has defeated Austria and
is the leading power in Europe.
Peace of
Luneville.
France has defeated Austria and
is the leading power in Europe.
Here is the map
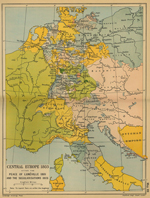
Map of Central Europe in 1803 after the Peace of Lunéville
(Treaty of Luneville) 1801 |
| |
|
| |
|
|
July
15, 1801 |
 Concordat
of 1801 between
France (Napoleon) and the
Vatican.
Concordat
of 1801 between
France (Napoleon) and the
Vatican. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
September 2, 1801 |
The
 Egyptian
Campaign ends.
Egyptian
Campaign ends. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
March
27, 1802 |
 Treaty of
Amiens
Treaty of
Amiens
|
| |
The
 War
of the Second Coalition
ends. War
of the Second Coalition
ends.
|
| |
The French Revolutionary Wars
are over. |
| |
|
More detailed
timelines here:
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1792
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1792
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1793
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1793
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1794
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1794
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1795
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1795
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1796
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1796
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1797
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1797
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1798
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1798
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1799
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1799
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1800
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1800
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1801
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1801
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1802
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1802
And here is a chart of the
 French armies from
1791-1802, their creation, their
commanders, their timeline.
French armies from
1791-1802, their creation, their
commanders, their timeline.
What Happened After the French Revolutionary
Wars?
Once the Revolutionary Wars had been fought,
the
 Napoleonic Wars came
next. Napoleonic Wars came
next.
French Revolutionary Wars and
Income Tax
In 1799, Great Britain became the
first country to charge a general income tax. The tax was imposed to
pay for Britain's participation in this war.
 Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs
tells us:
Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs
tells us:
Income Tax was
announced in 1798, and introduced in 1799,
as a means of paying for the war against the
French forces under Napoleon. France was
threatening to invade, and had already
landed briefly in Wales and Ireland. For
much of his campaigns from 1795, Napoleon
was better organised than the British
forces. The cost of war had drained
Britain’s resources, and run up a
considerable national debt. The army was
starving, and poor conditions in the navy in
1797 had led to mutiny.
 William Pitt the Younger was Prime Minister
and Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1783,
and needed greater ‘aid and contribution for
the prosecution of the war’.
William Pitt the Younger was Prime Minister
and Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1783,
and needed greater ‘aid and contribution for
the prosecution of the war’.
‘Certain duties upon income’ as outlined in
the Act of 1799 were to be the (temporary)
solution. It was a tax to beat Napoleon.
Income tax was to be applied in Great
Britain (but not Ireland) at a rate of 10%
on the total income of the taxpayer from all
sources above £60, with reductions on income
up to £200.
It was to be paid in six equal instalments
from June 1799, with an expected return of
£10 million in its first year. It actually
realised less than £6 million, but the money
was vital and a precedent had been set.
Reference Maps on the French Revolutionary Wars
1790 France
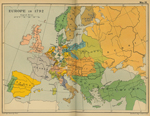
1792 Europe
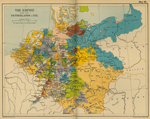
1792
Central Europe
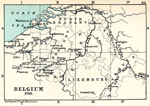
1792 Belgium
Here is a map of
Eastern France in 1792:
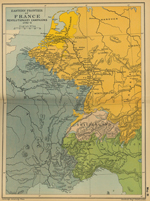
EASTERN FRONTIER OF FRANCE
REVOLUTIONARY CAMPAIGNS 1792 - 1795
Click to enlarge
Here comes a map of the Rhine country:
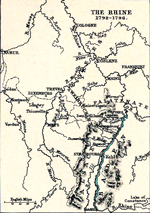
Rhine River
1792 - 1796
Click map to enlarge
Map for the naval engagements:
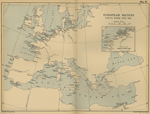
1792-1815
European Waters
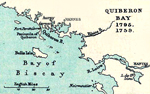
1795 Battle of
Quiberon Bay - June 27
These are maps of Napoleons Campaigns in Northern Italy in 1796-1797:
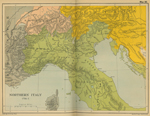
Northern
Italy 1796-1797
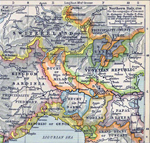
1796-1805
Northern Italy
1796 - 1805
Northern Italy and Switzerland
This map here is of Central Europe in
1797 after the
 Peace of Basel and of Campo Formio. The Peace of Basel and of Campo Formio. The
 Treaty of Campo Formio was
signed on October 17, 1797, after Napoleon had defeated Austria in
his first Italian campaign. Treaty of Campo Formio was
signed on October 17, 1797, after Napoleon had defeated Austria in
his first Italian campaign.

Central
Europe 1797
And then some...
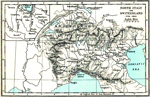
1798-1801 War of the Second Coalition
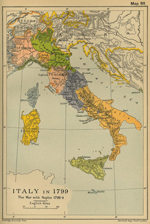
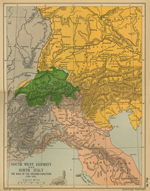
1799 Italy
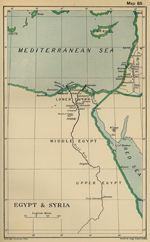
1798 Egypt and Syria
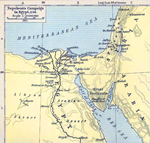
1798
Egypt and Syria
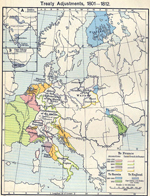
1801-1812
Treaties
More History
|