|
French
Revolutionary Wars Timeline:
1794
Go here for the
 French Revolutionary Wars
in a Nutshell.
French Revolutionary Wars
in a Nutshell.
January 6, 1794
Ferrand is the new commander of
the
 Army of the North. His post is
temporary.
Army of the North. His post is
temporary.
January 14, 1794
Michaud is the new commander of
the
 Army of the Rhine.
Army of the Rhine.
January 16, 1794
Dugommier is the new commander
of the
 Army of the Eastern Pyrenees.
Army of the Eastern Pyrenees.
January 21, 1794
Alexandre Dumas is the new
commander of the
 Army of the Alps.
Army of the Alps.
January 24, 1794
French
General Luckner was guillotined
today.
January 24, 1794
 Talleyrand,
residing in London, is told to leave Britain within five days. He
will get an extension and eventually leave for the United States on
March 2, 1794.
Talleyrand,
residing in London, is told to leave Britain within five days. He
will get an extension and eventually leave for the United States on
March 2, 1794.
January 27, 1794
Pichegru is the new commander of
the
 Army of the North. He also has
the command over the
Army of the North. He also has
the command over the
 Army of the Ardennes.
Army of the Ardennes.
February
3, 1794
The envoys from Saint Domingue (Louis-Pierre
Dufay, a white deputy,
Jean-Baptiste Mills, of mixed race, and
Jean-Baptiste Belley, a former
black slave) arrive and are admitted before the Convention at Paris.
February 4, 1794
The National Convention decrees the abolition of slavery in all
French colonies, except Bourbon Island (Reunion) and the Mascarene
Islands in the Indian Ocean.
This is the first abolition. It will
be revoked in 1802. The second, and final, abolition will be passed in
1848.
For more about the events of February
3 and 4, 1794, see also the
 Haitian Revolution.
Haitian Revolution.
February 12, 1794
The National Convention decrees that Marseille will keep its name.
For a while it was called The City Without a Name (Ville
sans nom), thanks to Louis Marie
Stanislas Fréron, who wanted to illustrate what would
happen to people who oppose the revolution.
February 15, 1794
The drapeau tricolore is the official French flag, with blue
and red (the colors of Paris) and white (the color of royalty),
arranged in three equal stripes and, following the recommendation of
the painter David, the blue should always be attached to the mast.
Already, these colors had been sported
by King Louis XVI on July 17, 1789.

The Tricolore
February 26, 1794
The National Convention passes the Ventose Decrees (Décrets
de Ventôse), part 1 of 2. In the French republican calendar,
today is 8 Ventôse, year II.
March 2, 1794
 Talleyrand
leaves for the United States.
Talleyrand
leaves for the United States.
March 3, 1794
The National Convention passes the Ventose Decrees (Décrets
de Ventôse), part 2 of 2. In the French republican calendar,
today is 13 Ventôse, year II.
The Ventose Decrees legalize the
confiscation of property from enemies of the State for the
distribution among the poor.
March 12, 1794
Poland erupts in an uprising against Russia and Prussia, led by
Tadeusz Kosciuszko.
March 19, 1794
 Jean-Baptiste Jourdan becomes commander of the Army
of the Moselle, succeeding
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan becomes commander of the Army
of the Moselle, succeeding
 General Lazare Hoche,
who will be arrested on March 22, 1794.
General Lazare Hoche,
who will be arrested on March 22, 1794.
March 22, 1794
 General Lazare Hoche
is arrested.
General Lazare Hoche
is arrested.
March 24, 1794
Jacques
René Hébert — main man of the
 sansculottes,
leader of the
sansculottes,
leader of the
 Club of the
Cordeliers, supporter of the Club of the
Cordeliers, supporter of the
 Reign of Terror
— and 17 revolutionaries who agreed
with him, are Reign of Terror
— and 17 revolutionaries who agreed
with him, are
 guillotined.
guillotined.
April 1794
The Army of the Moselle, led
by
 Jean-Baptiste Jourdan,
and the Army of the North, led by
Charles
Pichegru, join and invade
the
Austrian Netherlands
(approx. today's Belgium and
Luxembourg).
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan,
and the Army of the North, led by
Charles
Pichegru, join and invade
the
Austrian Netherlands
(approx. today's Belgium and
Luxembourg).
April 4, 1794
Fresh out of winter camp, France
resumes the war against Spain and
the Roussillon Campaign. They will
even invade Catalonia.
Horatio Nelson is made commander of
the bombardment on Bastia, Corsica.
April 5, 1794
 Georges Danton
(First President of the
Georges Danton
(First President of the
 Committee of Public Safety)
and Camille
Desmoulins (supported the
Committee of Public Safety)
and Camille
Desmoulins (supported the
 storming of the
Bastille, the
abolition of the monarchy, but dared to criticize the Committee of
Public Safety) are
storming of the
Bastille, the
abolition of the monarchy, but dared to criticize the Committee of
Public Safety) are
 guillotined. guillotined.
April 20, 1794
 Josephine de Beauharnais,
future wife of
Josephine de Beauharnais,
future wife of
 Napoleon Bonaparte,
is arrested and imprisoned at the Prison des Carmes,
a former convent of the Carmelites. She will
have to stay here until August 6, 1794.
Napoleon Bonaparte,
is arrested and imprisoned at the Prison des Carmes,
a former convent of the Carmelites. She will
have to stay here until August 6, 1794.
May 7, 1794
The worship of the Supreme Being is
set up and made law by decree.
"The French people recognize the existence
of the Supreme Being and the immortality of
the soul. They recognize that the worship
worthy of the Supreme Being is the practice
of the duties of man."
As annual national holidays are
declared:
July
14, 1789 (fall of the Bastille)
August
10, 1792 (overthrow of the monarchy)
January 21, 1793 (execution of Louis
XVI)
and
May 31, 1793 (purge of the
Girondins)
May 8, 1794
Antoine Laurent Lavoisier
(French chemist and tax farmer) is
 guillotined.
guillotined.
May 10, 1794
Princess
Elizabeth of France (Louis XVI's baby sister) is
 guillotined.
guillotined.
May 18, 1794
 Battle of Tourcoing.
French victory. Battle of Tourcoing.
French victory.
May 22, 1794
Battle of
Tournai.
May 23, 1794
Bastia, Corsica, surrenders to the British.
June 1, 1794
Battle of the
First of June
This battle is also called the
Battle of
the Glorious First of June
or the
Second Battle of Ushant
(the First Battle of Ushant having
been fought back in July 1778.)
This
is the first
naval battle of the French
Revolutionary Wars, fought between
the French fleet, led by
Admiral
Louis Thomas Villaret de Joyeuse
and the British fleet, led by
Admiral
Richard Howe, off
Ouessant Island, also called Ushant
Island, located 20 miles west off
Brest, Bretagne. The French fleet
escorted a grain convoy from
America.
British victory, but the French
performed surprisingly well. The
grain gets to France.
June 3, 1794
 General Jourdan
is appointed commander of the
Army of the Sambre and Meuse. This Army combined
General Jourdan
is appointed commander of the
Army of the Sambre and Meuse. This Army combined
the former left wing of the
Army of the Moselle,
the former right wing of the
Army of the North,
and the entire Army of the
Ardennes.
June 8, 1794
 Festival of the Supreme Being (Fête
de l’Être Suprême)
Festival of the Supreme Being (Fête
de l’Être Suprême)
June 10, 1794
The last six weeks of the Reign
of Terror begin today, also called the
Great
Terror.
Today a new law has been created,
stripping a suspect of all of his or her rights.
From now on, there is no right to a defense
lawyer and no right to a hearing. The only
punishment is the death penalty.
In the French
republican calendar, today is 22 Prairial, year
II. Hence, the new law is the
Law of 22 Prairial.
June 15, 1794
With
 Pascal Paoli's
blessing, the British set up an Anglo-Corsican
kingdom on
Pascal Paoli's
blessing, the British set up an Anglo-Corsican
kingdom on
 Corsica. Corsica.
The British, who
had to evacuate Toulon on December 19 1793,
succeeded in breaking the French resistance at
Bastia, Calvi, and Saint-Florent.
The island will be
back in firm French hands by October 1797.
June 17, 1794
Austrian's field marshal
Clerfayt tried to
relieve the French
Siege
of Ypres, but
couldn't pull it off. The siege
ends when its garrison
capitulates on June 17. The
French, led by
General
Pichegru, take the
town two days later.
June 26, 1794
 Battle of Fleurus.
Important French victory. For
the next twenty years, France,
instead of Austria, will occupy
the Low Countries. Battle of Fleurus.
Important French victory. For
the next twenty years, France,
instead of Austria, will occupy
the Low Countries.
Men of the day are
French Generals
 Jourdan and
Jourdan and
 Kleber.
Kleber.
June 29, 1794
The right wing of
the Army of the North and the left wing of the
Army of the Moselle are merged and called the
 Army of Sambre-et-Meuse
(Armée de Sambre-et-Meuse). Commander:
Army of Sambre-et-Meuse
(Armée de Sambre-et-Meuse). Commander:
 Jourdan.
Jourdan.
July 5, 1794
The
 Duke of York
and
Duke of York
and
 Coburg
meet just outside of Waterloo.
Frederick, the Duke of York,
recommended the ridge right there as
a good position to defend Brussels.
Frederick, the Prince of Coburg,
rejected the idea and Brussels was
again abandoned by the Austrians.
Coburg
meet just outside of Waterloo.
Frederick, the Duke of York,
recommended the ridge right there as
a good position to defend Brussels.
Frederick, the Prince of Coburg,
rejected the idea and Brussels was
again abandoned by the Austrians.
The British will withdraw
direction north
to the Waal River and the
Austrians will retreat to the east. The
French, in turn, will follow up
their victory with an advance into the
Rhineland.
July 12, 1794
British
Horatio Nelson loses his right eye during
preparations to capture Calvi, Corsica. Ever the
tough bone, he reports, "However the blemish is
nothing, not to be perceived unless told."
In 1795, he will
point out that he "can see very well with the
other."
July 25, 1794
First French assault on San
Sebastian and siege situation.
July 27, 1794
Antwerp falls. The Dutch in the
Austrian Netherlands surrender.
In Paris, the
 Revolution of the 9th Thermidor,
year II, takes place. The
Revolution of the 9th Thermidor,
year II, takes place. The
 National
Convention (the French
parliament) reasserts its power. Paris is done
with Robespierre's National
Convention (the French
parliament) reasserts its power. Paris is done
with Robespierre's
 Reign
of Terror. Reign
of Terror.
July 28, 1794
 Maximilien de Robespierre,
Louis de Saint-Just,
and others
are guillotined. The
Maximilien de Robespierre,
Louis de Saint-Just,
and others
are guillotined. The
 Reign
of Terror is officially over. Reign
of Terror is officially over.
August 2, 1794
James Monroe
arrives in Paris to replace
Gouverneur Morris
as Minister Plenipotentiary.
August 4, 1794
The French
take San Sebastian.
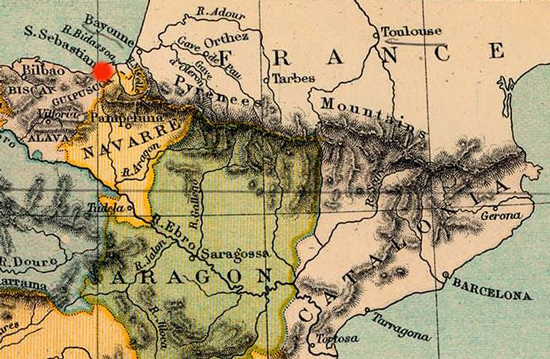
Map Location of San Sebastian
Click to
enlarge
August 6, 1794
 Josephine de Beauharnais
is released from the Prison des Carmes.
She had been a prisoner here since April 20,
1794.
Josephine de Beauharnais
is released from the Prison des Carmes.
She had been a prisoner here since April 20,
1794.
August 9, 1794
The French take Trier.
August 10, 1794
Calvi, Corsica, surrenders to the
British. Nelson earned it, having given his
right eye for this.
August 13, 1794
In his capacity as Minister
Plenipotentiary, James
Monroe addresses the National
Convention about the Franco-American friendship.
September 23, 1794
The French take Aachen (Aix-la-Chapelle) for the
second time.
October 2, 1794
 Battle of
Aldenhoven.
French victory.
Battle of
Aldenhoven.
French victory.
October 3, 1794
Having had to stomach the execution
of his sister
 Marie Antoinette
a year ago,
Maximilian Francis (German:
Max Franz) is eager to avoid a
personal encounter
with the French. He abandons his
home at Bonn and escapes first
to Dorsten, then to other
destinations. Finally in
1800 he will arrive back at
Vienna. Marie Antoinette
a year ago,
Maximilian Francis (German:
Max Franz) is eager to avoid a
personal encounter
with the French. He abandons his
home at Bonn and escapes first
to Dorsten, then to other
destinations. Finally in
1800 he will arrive back at
Vienna.
October 6, 1794
The
French take Cologne. For the
proud city of Cologne, this
means enemy occupation for the
first time since 900 years.
Also, on this day, the French
shell Dusseldorf from the left
side of the Rhine River.
Bombardment will continue until
tomorrow.
October 8, 1794
The
French take Bonn without a fight
and won't leave until January
1814.
October 23, 1794
The
French take Coblenz.
November 5, 1794
Thanks
to the U.S. Minister Plenipotentiary, James
Monroe, Thomas Paine gets out of prison today.
November 19, 1794
At
London, representatives of the United States and
Great Britain sign the
 Jay Treaty, also known as
the Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation.
Jay Treaty, also known as
the Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation.
France will see
this as direct violation of their 1778 treaties
and retaliate.
December 27, 1794
Pichegru and his army enter
Holland and arrive just south of Rotterdam.
More History
|